Ledger structure¶
At the core, an Openchain ledger is a key-value store, represented by records. At the data store level, record keys can be any arbitrary byte string, however Openchain Ledger expects a well defined structure for the record keys.
Record keys¶
Record keys are UTF8-encoded strings. They are structured in three parts, separated by colons (:).
- The record path: A path in the account hierarchy indicating where the record is situated.
- The record type: A value indicating the type of the record.
- The record name: The name of the record.
The combination of these three values uniquely identify a record.
Example 1¶
/p2pkh/mfiCwNxuFYMtb5ytCacgzDAineD2GNCnYo/:ACC:/asset/p2pkh/n15g8F3sVLufwvPmmX7tYPWrGGbGSbcaEB/
The path is /p2pkh/mfiCwNxuFYMtb5ytCacgzDAineD2GNCnYo/, the record type is ACC and the record name is /asset/p2pkh/n15g8F3sVLufwvPmmX7tYPWrGGbGSbcaEB/.
Example 2¶
/:DATA:info
The path is / (root path), the record type is DATA and the record name is info.
Account hierarchy¶
Openchain uses a hierarchy of accounts, similar to a file system. This adds a lot of interesting management options that systems like Bitcoin don’t have.
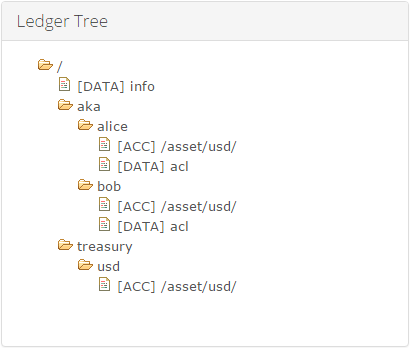
Accounts are identified by a path.
Account paths¶
The syntax for an account path follows a number of rules:
- Account paths start with the character
/. - Account paths end with the character
/. - Sections of an account path are separated by the character
/. - Sections of an account path may only contain alphanumeric characters and characters from the following set:
$-_.+!*'(),.
Record types¶
There are two valid record types as of this version of Openchain.
ACC record¶
The ACC record is used for representing a balance for a given asset type. The name of the record must be a path that represents the asset type. The value must be a 64-bits signed integer encoded in big endian. The value represents the current balance for the given account and the given asset type.
DATA record¶
The DATA record is used to store arbitrary text data. The record name can be any valid UTF-8 string. It can be used to store things such as asset metadata, symbolic links within the accounting system, permissions, or any other important piece of arbitrary data that needs to be cryptographically secure.